
In 1972, the Federal Election Campaign Act (FECA) was enacted into law. This law created the Federal Election Commission (FEC) and has been the subject of vociferous litigation ever since. The Court's most recent pronouncement came in 2014's McCutcheon v. FEC. On First Amendment grounds, the McCutcheon majority struck down certain caps on individual contributions.
This map shows a Spaeth Visualization of the 3-degree citation networks linking McCutcheon as well as the controverisal 2010 Citizens United decision to the Court's first FECA case, Buckley v. Valeo (1976). Since these networks were very large, I filtered out all cases that did not include the text "federal election campaign act". After this filtering process, I manually took out "orphan opinions" -- ones that did not cite to other cases in the network. This map shows just how divisive these cases are. The average degree of dissent is 0.62. If you only count cases decided from 1986 onwards, the degree of dissent in the network increases to 0.79! The map gives visual representation to the reality that campaign finance is a highly divisive area of doctrine.
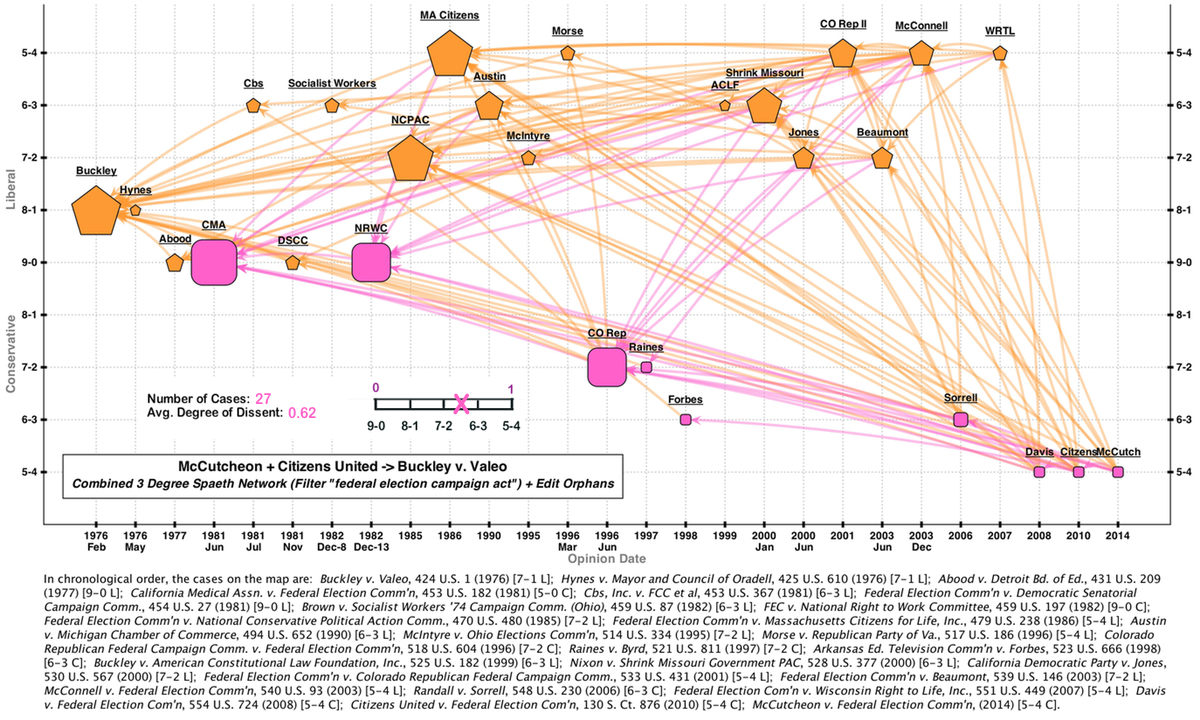
To open a full-sized version of this map -- complete with links to the underlying opinions -- please click here.
Please see this blog post for an analyis of the cases in this map.

This map provides a glimpse at the lines of dissent that lead to the establishment of modern commercial speech doctrine in 1976's Virginia Pharmacy Board case. The map shows that the decision to grant commercial speech First Amendment protection was presaged by Justice Douglas' 1959 concurrence in Cammarano was then was given new life and impetus by the highly contentious Pittsburg Press Co. case.
This map shows the main cases in the Court's modern "commercial speech" line and is based on Sullivan & Feldman First Amendment text (5th Ed. 2013). This map uses a Spaeth projection. For a detailed discussion of the context for this map, see this blog post.
This map was generated for the students in Prof. Starger's Constitutional Law II class. It charts the cases regarding libel, privacy torts, and IIED in the Sullivan & Feldman First Amendment text (pp. 94-125 of 5th Ed). This map uses a Spaeth Projection. Please click on the map open a full-sized version of the map complete with links to the underlying case opinions.
This map is a hyperlinked interpretation of a classic First Amendment line from Schenck (1919) to Brandenburg (1969). Click on map for full interactive version. For further explanation, please see this In Progress post.
This map shows the citation network connecting the 2014 legislative prayer case Town of Greece with the 1983 legislative prayer case Marsh v. Chambers to 3 degrees.
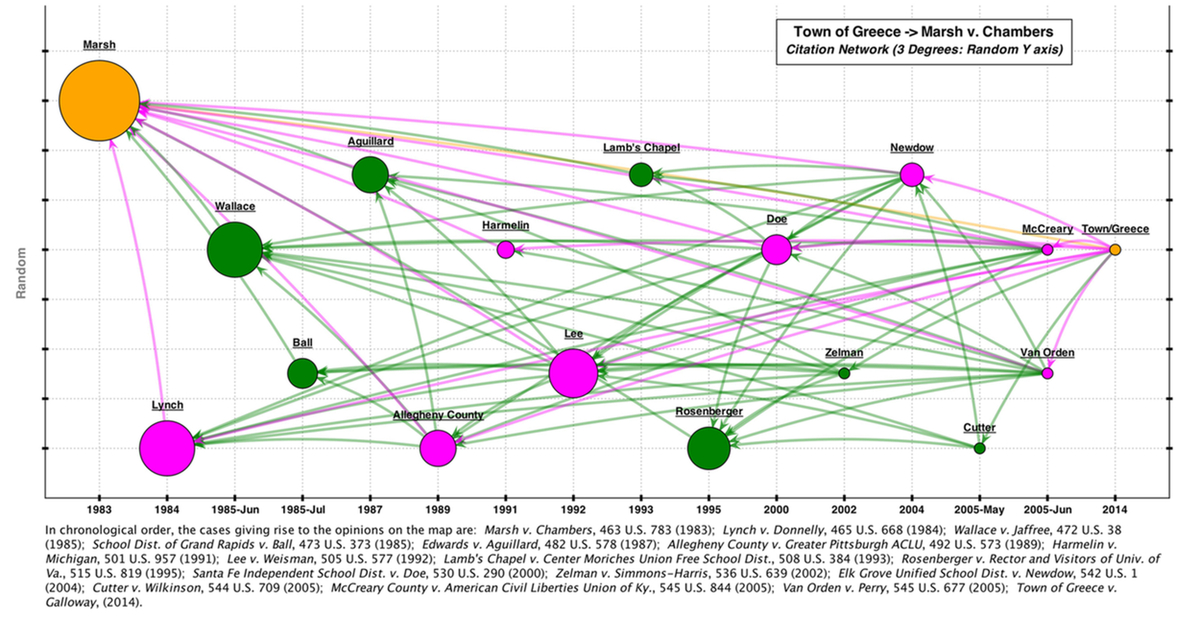
To open a full-sized version of this map -- complete with links to the underlying opinions -- please click here.
This map shows the citation network connecting the 2014 legislative prayer case Town of Greece with the 1983 legislative prayer case Marsh v. Chambers using a Spaeth Visualization based on a 3 degrees network. The map was edited by hand to add the authors of the majority opinions. There are 17 cases in the network, with an average degree of dissent of .75.
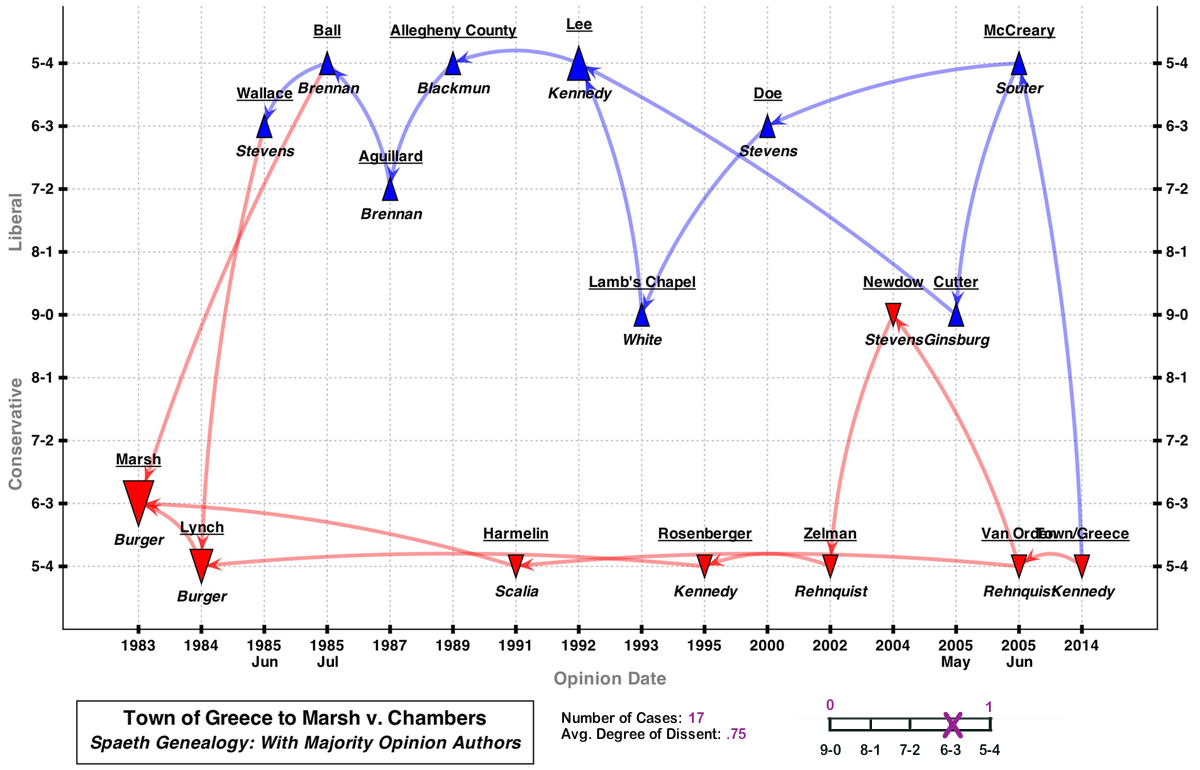
To open a full-sized version of this map -- complete with links to underlying opinions -- please click here.
In 1972, the Federal Election Campaign Act (FECA) was enacted into law. This law created the Federal Election Commission (FEC) and has been the subject of vociferous litigation ever since. The Court's most recent pronouncement came in 2014's McCutcheon v. FEC. On First Amendment grounds, the McCutcheon majority struck down certain caps on individual contributions.
This map shows a Spaeth Visualization of the 3-degree citation networks linking McCutcheon as well as the controverisal 2010 Citizens United decision to the Court's first FECA case, Buckley v. Valeo (1976). Since these networks were very large, I filtered out all cases that did not include the text "federal election campaign act". After this filtering process, I manually took out "orphan opinions" -- ones that did not cite to other cases in the network. This map shows just how divisive these cases are. The average degree of dissent is 0.62. If you only count cases decided from 1986 onwards, the degree of dissent in the network increases to 0.79! The map gives visual representation to the reality that campaign finance is a highly divisive area of doctrine.

To open a full-sized version of this map -- complete with links to the underlying opinions -- please click here.
To see a full-sized image of this map -- complete with links to the underlying opinions -- please click here.
The Supreme Court's 2014 Hobby Lobby decision was one of last Term's most controversial cases. At its most basic level, Hobby Lobby concerned the interpretation of RFRA - the Religious Freedom Restoration Act, a law passed by Congress in 1993 in direct response to the Supreme Court's decision in Employment Division v. Smith. The map above shows the 3-degree citation network connecting Hobby Lobby to Smith. To fill out the network, the map was combined with the 3-degree network connecting Hobby Lobby to 1993's Church of Lukumi Babalu Aye. Please note that the combined network originally contained 17 cases. Five cases were filtered out because they did not contain the phrase "free exercise."
The map now shows the network of post-Smith decisions implicating the First Amendment issue in Hobby Lobby. This is presented as a random network (the Y axis has no meaning; for explanation of this concept please watch this video). Blue cases are the first degree connections. Magenta cases are the second degree connections. Green cases are the third degree connections. To view the opinion text for any of the cases, click on the map above and then click on cases.
| Doctrinal Area | Recent Case | Older Case |
| Mistaken Retaliation | Heffernan (2016) | Letter Carriers (1973) |
| License Plate Speech | Confederate Veterans (2015) | Perry Ed (1983) |
| Sign Codes | Reed (2015) | Con Ed (1980) |
| Judicial Candidate Speech | Williams-Yulee (2015) | Eu (1989) |
| Campaign Finance | AZ Free Enterprise (2012) | Buckley (1976) |
| Campaign Finance | McCutcheon (2014) | Buckle (1976) |
| Anti-abortion Speech | McCullen (2014) | Madsen (1994) |
| Commercial Speech | Sorrell (2011) | Valentine (1942) |
| Commerical Speech | Sorrell (2011) | VA Pharmacy Board (1976) |
| New Media | FCC v. Fox (2009) | Rowan (1970) |
| Libel, Privacy, IIED | Alvarez (2012) | New York Times (1964) |
| Incitement | Brandenburg (1969) | Schenck (1919) |
| Leglslative Prayer | Town of Greece (2014) | Marsh (1983) |
| Campaign Finance | McCucheon (2014) | Buckley (1976) |
| Free Exercise | Hobby Lobby (2014) | Smith (1992) |